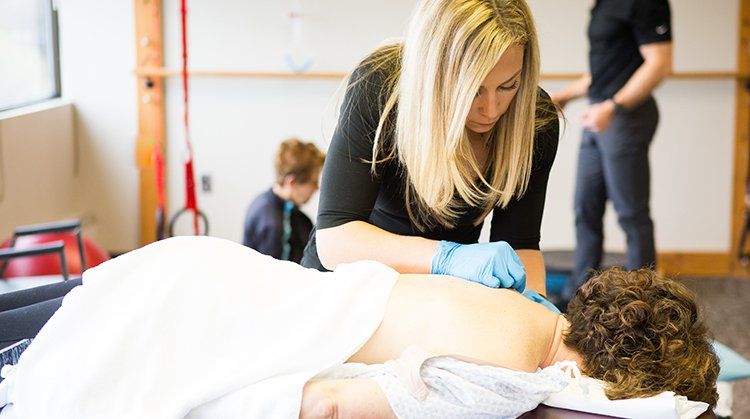






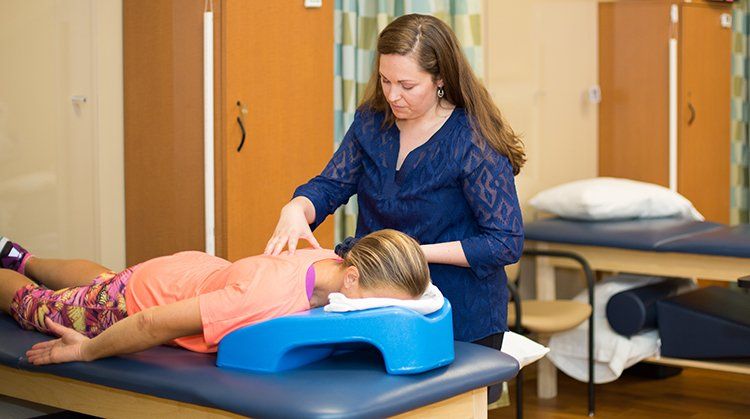

Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) refers to pain at the front of the knee, in and around the kneecap (patella). PFPS is one of the most common types of knee pain experienced in the United States, particularly among athletes, active teenagers, older adults, and people who perform physical labor. Patellofemoral pain affects more women than men and accounts for 20% to 25% of all reported knee pain. Physical therapists design exercise and treatment programs for people experiencing PFPS to help them reduce their pain, restore normal movement, and avoid future injury.
Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) refers to pain at the front of the knee, in and around the kneecap. (The kneecap, or patella, is the triangle-shaped bone at the front of the knee joint.) Pain occurs when friction is created between the undersurface of the kneecap and the thigh bone (femur). The pain also is usually accompanied by tenderness along the edges of the kneecap.
Current research indicates that PFPS is an "overuse syndrome," which means that it may result from repetitive or excessive use of the knee. Other contributing factors may include:
These conditions can interfere with the ability of the kneecap to glide smoothly on the femur (the bone that connects the knee to the thigh) in the femoral groove (situated along the thigh bone) during movement. The friction between the undersurface of the kneecap and the femur causes the pain and irritation commonly seen in PFPS. The kneecap also may fail to track properly in the femoral groove when the quadriceps muscle on the inside front of the thigh is weak, and the hip muscles on the outside of the thigh are tight. The kneecap gets pulled in the direction of the tight hip muscles and can track or tilt to the side, which irritates the tissues around the kneecap.
PFPS often occurs in people who are physically active or who have suddenly increased their level of activity, especially when that activity involves repeated knee motion, such as running, stair climbing, squatting, or repeated carrying of heavy loads. Older adults may experience age-related changes that cause the cartilage on the undersurface of the kneecap to wear out, resulting in pain and difficulty completing daily tasks without pain.
People with PFPS may experience:
Your physical therapist will review your health history, perform a thorough examination, and conduct a series of tests to evaluate the knee. Your therapist may observe the alignment of your feet, analyze your walking and running patterns, and test the strength of your hip and thigh muscles to find out whether there is a weakness or imbalance that might be contributing to your pain. Your physical therapist also will check the flexibility of the muscles in your leg, paying close attention to those that attach at the knee.
Generally, X-rays are not needed to diagnose PFPS. Your physical therapist may consult with an orthopedic physician who may order an X-ray to rule out other conditions.
After a comprehensive evaluation, your physical therapist will analyze the findings and, if PFPS is present, your therapist will prescribe an exercise and rehabilitation program just for you. Your program may include:
Strengthening exercises. Your physical therapist will teach you exercises targeted at the hip (specifically, the muscles of the buttock and thigh), the knee (specifically, the quadriceps muscle located on the front of your thigh that straightens your knee), and the ankle. Strengthening these muscles will help relieve pressure on the knee, as you perform your daily activities.
Stretching exercises. Your physical therapist also will choose exercises to gently stretch the muscles of the hip, knee, and ankle. Increasing the flexibility of these muscles will help reduce any abnormal forces on the knee and kneecap.
Positional training. Based on your activity level, your physical therapist may teach you proper form and positioning when performing activities, such as rising from a chair to a standing position, stair climbing, squatting, or lunging, to minimize excessive forces on the kneecap. This type of training is particularly effective for athletes.
Cross-training guidance. PFPS is often caused by overuse and repetitive activities. Athletes and active individuals can benefit from a physical therapist’s guidance about proper cross-training techniques to minimize stress on the knees.
Taping or bracing. Your physical therapist may choose to tape the kneecap to reduce your pain and retrain your muscles to work efficiently. There are many forms of knee taping, including some types of tape that help align the kneecap and some that just provide mild support to irritated tissues around it. In some cases, a brace may be required to hold the knee in the best position to ensure proper healing.
Electrical stimulation. Your physical therapist may prescribe treatments with gentle electrical stimulation to reduce pain and support the healing process.
Activity-based exercises. If you are having difficulty performing specific daily activities, or are an athlete who wants to return to a specific sport, your physical therapist will design individualized exercises to rebuild your strength and performance levels.
Fitting for an orthosis. If the alignment and position of your foot and arch appear to be contributing to your knee pain, your physical therapist may fit you with a special shoe insert called an orthosis. The orthosis can decrease the stress to your knee caused by low or high arches.
PFPS is much easier to treat if it is caught early. Timely treatment by a physical therapist may help stop any underlying problems before they become worse. If you are experiencing knee pain, contact a physical therapist immediately.
Your physical therapist can show you how to adjust your daily activities to safeguard your knees, and teach you exercises to do at home to strengthen your muscles and bones—and help prevent PFPS.
Physical therapists can assess athletic footwear and recommend proper choices for runners and daily walkers alike. Wearing the correct type of shoes for your activity and changing them when they are no longer supportive is essential to injury prevention.
Amelia is a 25-year-old office assistant who loves to start her day with a 5-mile run. Over the past 6 months, she has been training for her first marathon. She began by training on very flat ground and has just moved to a hilly area.
Last week, Amelia began feeling pain in the front of her left knee when running downhill. Today, she had to stop running after 3 miles because of her knee pain. She called her physical therapist.
Amelia's physical therapist completes a comprehensive evaluation, including a screening for other possible conditions that might be causing her pain. He uses special tests to measure her strength and finds that she has weak hip muscles and tenderness around the kneecap. He determines that she has developed PFPS. Amelia is shocked to learn that she also has flat feet, and she’s not wearing the right supportive running shoes.
To begin her treatments, Amelia’s physical therapist applies special tape to the front of her knee to help reduce her pain, and instructs her in the use of ice to decrease her symptoms. He performs gentle movements of her kneecap and the surrounding tissues to help increase mobility and decrease pain. He teaches her special exercises to gently strengthen the weak muscles that support the knee.
He also designs a specific home-exercise program for Amelia to perform between sessions. He provides information about proper shoe choices for her foot and body type, and advises her to purchase shoes that will give her feet the right type of support. He also recommends that she try deep-water running or swimming for a week instead of her regular running program, until her condition improves.
After her first week of physical therapy, Amelia notices a decrease in her pain and an increased ability to walk up and down stairs without pain. Her physical therapist approves her new footwear, and adds more challenging exercises to her session and her home program. He gives her the go-ahead to race-walk. She applies ice only when she has pain.
After 2 weeks, Amelia reports she is feeling even less pain. Her physical therapist continues to increase the intensity of her exercises, and she starts to run again—but only on flat surfaces and short distances combined with longer walk intervals.
After a few more weeks of therapy, Amelia occasionally feels only slight twinges of pain and gradually resumes her prior level of training. Her physical therapist recommends continuation of her stretching and strengthening exercises, and discharges her from physical therapy.
A few months later, Amelia completes her first marathon pain free. She is thrilled to learn that her time was a personal best!
This story was based on a real-life case. Your case may be different. Your physical therapist will tailor a treatment program to your specific case.








